Python Continue StatementLast Updated : 3 Jan 2026 The continue statement in Python is used to skip the rest of the code inside a loop for the current iteration and proceed to the next iteration immediately. It is useful when some specified conditions need to be ignored without terminating or breaking out of the entire loop. The continue statement in Python is used in for and while loops to improve code efficiency and readability.  Syntax of the Continue Statement:The syntax of the Python Continue statement is as follows: When the continue statement is executed in Python, it enables the loop to skip the rest of the code in the current iteration and immediately advances to the next iteration. In the case of nested loops, the continue statement only affects the innermost loop. Simple Python Continue Statement ExampleLet's see a simple example to understand how the continue statement works: ExampleExecute NowOutput: 1 3 5 7 9 Explanation: In the above example, the continue statement is executed for every number known as num, which causes the program to skip the print(num) function and move on to the next iteration. Flowchart of the continue Statement in PythonThe following is the flowchart of the Python continue statement: 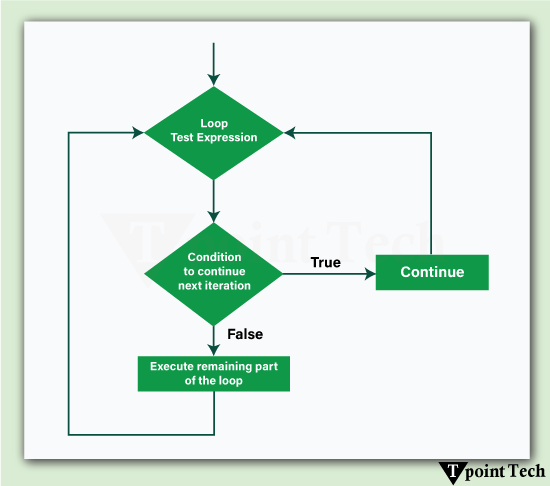 Explanation of the Flowchart of Python Continue Statement: Step 1: Initially, the loop starts. Step 2: The condition of the loop is checked. Step 3: If the 'continue' condition is achieved:
Step 4: Otherwise, the remaining loop body is executed. Step 5: The entire process gets repeated until the loop terminates. Different Examples of the continue StatementLet us now see some more examples showing the use of the continue statement in Python. Example 1: Skipping Specific ValuesLet us take an example to demonstrate how to skip specific value in Python using continue statement. ExampleExecute NowOutput: Pythn Prgramming Explanation: Here, the letter 'o' is skipped whenever it appears in the string. Example 2: Skipping Iterations in a while LoopLet us take an example to demonstrate how to skip iterations in while loop using the continue statement. ExampleExecute NowOutput: 1 2 3 4 6 7 8 9 10 Explanation: When x equals 5, the continue statement prevents print(x) from executing, and the loop proceeds with the next iteration. Example 3: Skipping Negative Numbers in a ListLet us take an example to demonstrate how to skip negative numbers in a list using the continue statement. ExampleExecute NowOutput: 10 5 7 Explanation: In this example, negative numbers are skipped, and only positive numbers are printed. Example 4: Skipping Certain Words in a SentenceLet us take an example to demonstrate how to skip certain words in a sentence using the continue statement. ExampleExecute NowOutput: Python learn Tpointtech Explanation: Here, the words "from" and "a" are skipped while printing the rest of the sentence. Example 5: Skipping Multiples of 3 in a RangeLet us take an example to demonstrate how to skip multiples of 3 in a range using the continue statement. ExampleExecute NowOutput: 1 2 4 5 7 8 10 11 13 14 16 17 19 Explanation: This example skips numbers that are multiples of 3 while printing the rest. Example 6: Skipping Empty Strings in a ListLet us take an example to demonstrate how to skip empty strings in a list using the continue statement.ExampleExecute NowOutput: apple banana cherry Advantages of Python Continue StatementThere are several advantages of using the Continue Statement in Python. Let's see some of them: 
ConclusionThe use of a specific loop iteration can be skipped by utilizing the "continue" statement in Python without exiting the iteration process. This comes in handy when certain conditions should be left out while processing other elements that form a sequence. The code structure becomes simple and makes comprehending the loops easier, which ultimately increases the efficiency of the program. Next TopicPython Break |
Subscribe to Tpoint Tech
We request you to subscribe our newsletter for upcoming updates.


