Abstract
Construction of a fault-tolerant quantum computer remains a challenging problem due to unavoidable noise and fragile quantum states. However, this goal can be achieved by introducing quantum error-correcting codes. Here, we experimentally realize an automated error correction code and demonstrate the nondestructive discrimination of GHZ states in IBM 5-qubit quantum computer. After performing quantum state tomography, we obtain the experimental results with a high fidelity. Finally, we generalize the investigated code for maximally entangled n-qudit case, which could both detect and automatically correct any arbitrary phase-change error, or any phase-flip error, or any bit-flip error, or combined error of all types of error.
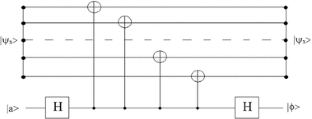




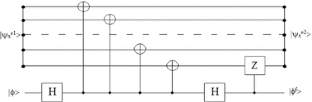












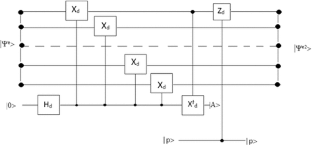
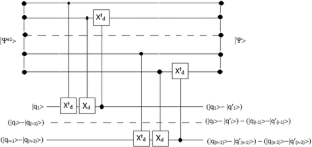
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nielsen, M.A., Chuang, I.L.: Quantum Computation and Quantum Information. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Crepeau, C., Jozsa, R., Peres, A., Wootters, W.K.: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1895 (1993)
Ghosh, S., Kar, G., Roy, A., Sarkar, D., Sen, U.: Entanglement teleportation through GHZ-class states. New J. Phys. 4, 48 (2002)
Muralidharan, S., Panigrahi, P.K.: Perfect teleportation, quantum-state sharing, and superdense coding through a genuinely entangled five-qubit state. Phys. Rev. A 77, 032321 (2008)
Choudhury, S., Muralidharan, S., Panigrahi, P.K.: Quantum teleportation and state sharing using a genuinely entangled six-qubit state. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 42, 115303 (2009)
Muralidharan, S., Karumanchi, S., Jain, S., Srikanth, R., Panigrahi, P.K.: 2N qubit “mirror states” for optimal quantum communication. Eur. Phys. J. D 61, 757–763 (2011)
Paul, N., Menon, J.V., Karumanchi, S., Muralidharan, S., Panigrahi, P.K.: Quantum tasks using six qubit cluster states. Quantum Inf. Process. 10, 619–632 (2011)
Muralidharan, S., Panigrahi, P.K.: Quantum-information splitting using multipartite cluster states. Phys. Rev. A 78, 062333 (2008)
Muralidharan, S., Karumanchi, S., Narayanaswamy, S., Srikanth, R., Panigrahi, P.K.: In how many ways can quantum information be split ? (2011). arXiv:0907.3532
Panigrahi, P.K., Karumanchi, S., Muralidharan, S.: Minimal classical communication and measurement complexity for quantum information splitting of a two-qubit state. Pramana J. Phys. 73, 499–504 (2009)
Muralidharan, S., Jain, S., Panigrahi, P.K.: Splitting of quantum information using N-qubit linear cluster states. Opt. Commun. 284, 1082–1085 (2010)
Nandi, K., Paul, G.: Quantum information splitting using a pair of GHZ states (2015). arXiv:1501.07529
Jain, S., Muralidharan, S., Panigrahi, P.K.: Secure quantum conversation through non-destructive discrimination of highly entangled multipartite states. Europhys. Lett. 87, 60008 (2009)
Prasath, E.S., Muralidharan, S., Mitra, C., Panigrahi, P.K.: Multipartite entangled magnon states as quantum communication channels. Quantum Inf. Process. 11, 397–410 (2012)
Agrawal, P., Pati, A.: Perfect teleportation and superdense coding with W states. Phys. Rev. A 74, 062320 (2006)
Moulick, S.R., Panigrahi, P.K.: Quantum cheques. Quantum Inf. Process. 15, 2475–2486 (2016)
Behera, B.K., Banerjee, A., Panigrahi, P.K.: Experimental realization of quantum cheque using a five-qubit quantum computer. Quantum Inf. Process. 16, 312 (2017)
Xia, Y., Fu, C.B., Zhang, S., Hong, S.K., Yeon, K.H.: Quantum dialogue by using the GHZ state. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 48(1), 24–27 (2006)
Cory, D.G., Price, M.D., Maas, W., Knill, E., Laflamme, R., Zurek, W.H., Havel, T.F., Somaroo, S.S.: Experimental quantum error correction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 2152 (1998)
Knill, E., Laflamme, R., Milburn, G.J.: A scheme for efficient quantum computation with linear optics. Nature 409, 46–52 (2001)
Chiaverini, J., Leibfried, D., Schaetz, T., Barrett, M.D., Blakestad, R.B., Britton, J., Itano, W.M., Jost, J.D., Knill, E., Langer, C., Ozeri, R., Wineland, D.J.: Realization of quantum error correction. Nature 432, 602–605 (2004)
Schindler, P., Barreiro, J.T., Monz, T., Nebendahl, V., Nigg, D., Chwalla, M., Hennrich, M., Blatt, R.: Experimental repetitive quantum error correction. Science 332, 1059–1061 (2011)
Reed, M.D., DiCarlo, L., Nigg, S.E., Sun, L., Frunzio, L., Girvin, S.M., Schoelkopf, R.J.: Realization of three-qubit quantum error correction with superconducting circuits. Nature 482, 382385 (2012)
Nigg, D., Müller, M., Martinez, E.A., Nigg, D., Schindler, P., Monz, T., Blatt, R., Martin-Delgado, M.A.: Iterative phase optimization of elementary quantum error correcting codes. Phys. Rev. X 6, 031030 (2016)
Müller, M., Rivas, A., Martinez, E.A., Schindler, P., Hennrich, M., Monz, T., Martin-Delgado, M.A., Blatt, R.: Quantum computations on a topologically encoded qubit. Science 345, 302–305 (2014)
Taghavi, S., Kosut, R.L., Lidar, D.A.: Channel-optimized quantum error correction. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 56, 1461–1473 (2010)
Bombin, H., Martin-Delgado, M.A.: Statistical mechanical models and topological color codes. Phys. Rev. A 77, 042322 (2008)
Kargarian, M., Bombin, H., Martin-Delgado, M.A.: Topological color codes and two-body quantum lattice Hamiltonians. New J. Phys. 12, 025018 (2010)
Gupta, M., Pathak, A., Srikanth, R., Panigrahi, P.K.: Non-destructive orthonormal state discrimination (2005). arXiv:quant-ph/0507096
Gupta, M., Pathak, A., Srikanth, R., Panigrahi, P.K.: General circuits for indirecting and distributing measurement in quantum computation. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 5, 62 (2007)
Sisodia, M., Shukla, A., Pathak, A.: Experimental realization of nondestructive discrimination of Bell states using a five-qubit quantum computer. Phys. Lett. A 381(46), 3860–3874 (2017)
Pandey, P., Prasath, S., Gupta, M., Panigrahi, P.K.: Automated error correction for generalized Bell states (2010). arXiv:1008.2129
Panigrahi, P.K., Gupta, M., Pathak, A., Srikanth, R.: Circuits for distributing quantum measurement. AIP Conf. Proc. 864, 197 (2006)
IBM Quantum Experience. https://www.research.ibm.com/ibm-q/
Wootton, J.R., Loss, D.: A repetition code of 15 qubits (2017). arXiv:1709.00990
Samal, J.R., Gupta, M., Panigrahi, P.K., Kumar, A.: Non-destructive discrimination of Bell states by NMR using a single ancilla qubit. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 43, 095508 (2010)
Manu, V.S., Kumar, A.: Non-destructive discrimination of arbitrary set of orthogonal quantum states by NMR using quantum phase estimation (2011). arXiv:quant-ph/1105.2186v1
Sisodia, M., Verma, V., Thapliyal, K., Pathak, A.: Teleportation of a qubit using entangled non-orthogonal states: a comparative study. Quantum Inf. Process. 16, 76 (2017)
Majumder, A., Mohapatra, S., Kumar, A.: Experimental realization of secure multiparty quantum summation using five-qubit IBM quantum computer on cloud (2017). arXiv:quant-ph/1707.07460v1
Kalra, A.R., Prakash, S., Behera, B.K., Panigrahi, P.K.: Experimental demonstration of the no hiding theorem using a 5 qubit quantum computer (2017). arXiv:quant-ph/1707.09462v1
Rundle, R.P., Mills, P.W., Tilma, T., Samson, J.H., Everitt, M.J.: Simple procedure for phase-space measurement and entanglement validation. Phys. Rev. A 96, 022117 (2017)
Grimaldi, D., Marinov, M.: Distributed measurement systems. Measurement 30, 279–287 (2001)
Gangopadhyay, S., Manabputra, Behera, B.K., Panigrahi, P.K.: Generalization and partial demonstration of an entanglement based Deutsch–Jozsa like algorithm using a 5-qubit quantum computer (2017). arXiv:1708.06375
Sisodia, M., Shukla, A., Thapliyal, K., Pathak, A.: Design and experimental realization of an optimal scheme for teleportion of an n-qubit quantum state. Quantum Inf. Process. 16, 292 (2017)
Vishnu, P.K., Joy, D., Behera, B.K., Panigrahi, P.K.: Experimental demonstration of non-local controlled-unitary quantum gates using a five-qubit quantum computer (2017). arXiv:1709.05697
Dash, A., Rout, S., Behera, B.K., Panigrahi, P.K.: A verification algorithm and its application to quantum locker in IBM quantum computer (2017). arXiv:1710.05196
Roy, S., Behera, B.K., Panigrahi, P.K.: Experimental realization of quantum violation of entropic noncontextual inequality in four dimension using IBM quantum computer (2017). arXiv:1710.10717
Satyajit, S., Srinivasan, K., Behera, B.K., Panigrahi, P.K.: Discrimination of highly entangled Z-states in IBM quantum computer (2017). arXiv:1712.05485
Li, R., Alvarez-Rodriguez, U., Lamata, L., Solano, E.: Approximate quantum adders with genetic algorithms: an IBM quantum experience. Quantum Meas. Quantum Metrol. 4, 1–7 (2017)
Wootton, J.R.: Demonstrating non-Abelian braiding of surface code defects in a five qubit experiment. Quantum Sci. Technol. 2, 015006 (2017)
Berta, M., Wehner, S., Wilde, M.M.: Entropic uncertainty and measurement reversibility. New J. Phys. 18, 073004 (2016)
Deffner, S.: Demonstration of entanglement assisted invariance on IBM’s quantum experience. Heliyon 3, e00444 (2016)
Huffman, E., Mizel, A.: Violation of noninvasive macrorealism by a superconducting qubit: Implementation of a Leggett–Garg test that addresses the clumsiness loophole. Phys. Rev. A 95, 032131 (2017)
Alsina, D., Latorre, J.I.: Experimental test of Mermin inequalities on a five-qubit quantum computer. Phys. Rev. A 94, 012314 (2016)
García-Martín, D., Sierra, G.: Five experimental tests on the 5-qubit IBM quantum computer (2017). arXiv:1712.05642
Das, S., Paul, G.: Experimental test of Hardy’s paradox on a five-qubit quantum computer (2017). arXiv:1712.04925
Balu, R., Castillo, D., Siopsis, G.: Physical realization of topological quantum walks on IBM-Q and beyond (2017). arXiv:1710.03615
Yalçinkaya, İ., Gedik, Z.: Optimization and experimental realization of quantum permutation algorithm. Phys. Rev. A 96, 062339 (2017)
Kandala, A., Mezzacapo, A., Temme, K., Takita, M., Brink, M., Chow, J.M., Gambetta, J.M.: Hardware-efficient variational quantum eigensolver for small molecules and quantum magnets. Nature 549, 242–246 (2017)
Alvarez-Rodriguez, U., Sanz, M., Lamata, L., Solano, E.: Quantum artificial life in an IBM quantum computer (2017). arXiv:1711.09442
Schuld, M., Fingerhuth, M., Petruccione, F.: Implementing a distance-based classifier with a quantum interference circuit (2017). arXiv:1703.10793
Behera, B.K., Seth, S., Das, A., Panigrahi, P.K.: Demonstration of entanglement purification and swapping protocol to design quantum repeater in IBM quantum computer (2017). arXiv:1712.00854
Behera, B.K., Reza, T., Gupta, A., Panigrahi, P.K.: Designing quantum router in IBM quantum computer (2018). arXiv:1803.06530
Viyuela, O., Rivas, A., Gasparinetti, S., Wallraff, A., Filipp, S., Martin-Delgado, M.A.: Observation of topological Uhlmann phases with superconducting qubits. npj Quantum Inf. 4, 10 (2018)
IBM quantum computing platform (userguide). https://quantumexperience.ng.bluemix.net/qx/user-guide
Chuang, I.L., Gershenfeld, N., Kubinec, M.G., Leung, D.W.: Bulk quantum computation with nuclear magnetic resonance: theory and experiment. Proc. R. Soc. 454, 447–467 (1998)
James, D.F., Kwiat, P.G., Munro, W.J., White, A.G.: Measurement of qubits. Phys. Rev. A 64, 052312 (2001)
Hebenstreit, M., Alsina, D., Latorre, J., Kraus, B.: Compressed quantum computation using a remote five-qubit quantum computer. Phys. Rev. A 95, 052339 (2017)
Filipp, S., Maurer, P., Leek, P., Baur, M., Bianchetti, R., Fink, J.M., Göppl, M., Steffen, L., Gambetta, J., Blais, A.: Two-qubit state tomography using a joint dispersive readout. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 200402 (2009)
Shukla, A., Rao, K., Mahesh, T.: Ancilla assisted quantum state tomography in many-qubit registers (2013). arXiv:quant-ph/1304.5851
Pathak, A.: Elements of Quantum Computation and Quantum Communication. Taylor & Francis, London (2013). ISBN:1466517913 9781466517912
Acknowledgements
DG and BKB are financially supported by DST Inspire Fellowship. PA would like to thank the National Initiative for Undergraduate Science (NIUS) Physics. The authors are extremely grateful to IBM team and IBM Quantum Experience project. This work does not reflect the views or opinions of IBM or any of its employees.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendix 1: Results of all above circuits in IBM quantum computer

Appendix 2: Calibration data of the IBM quantum computer

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghosh, D., Agarwal, P., Pandey, P. et al. Automated error correction in IBM quantum computer and explicit generalization. Quantum Inf Process 17, 153 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-018-1920-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-018-1920-z




